Abstract
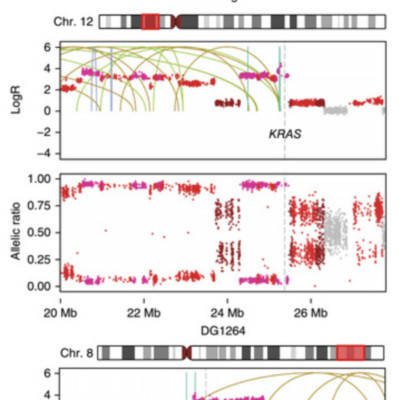
We studied the whole-genome point mutation and structural variation patterns of 133 tumors (59 high-grade serous (HGSC), 35 clear cell (CCOC), 29 endometrioid (ENOC), and 10 adult granulosa cell (GCT)) as a substrate for class discovery in ovarian cancer. Ab initio clustering of integrated point mutation and structural variation signatures identified seven subgroups both between and within histotypes. Prevalence of foldback inversions identified a prognostically significant HGSC group associated with inferior survival. This finding was recapitulated in two independent cohorts (n = 576 cases), transcending BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation and gene expression features of HGSC. CCOC cancers grouped according to APOBEC deamination (26%) and age-related mutational signatures (40%). ENOCs were divided by cases with microsatellite instability (28%), with a distinct mismatch-repair mutation signature. Taken together, our work establishes the potency of the somatic genome, reflective of diverse DNA repair deficiencies, to stratify ovarian cancers into distinct biological strata within the major histotypes.