Abstract
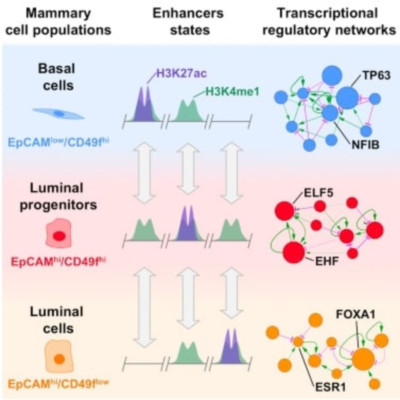
The normal adult human mammary gland is a continuous bilayered epithelial system. Bipotent and myoepithelial progenitors are prominent and unique components of the outer (basal) layer. The inner (luminal) layer includes both luminal-restricted progenitors and a phenotypically separable fraction that lacks progenitor activity. We now report an epigenomic comparison of these three subsets with one another, with their associated stromal cells, and with three immortalized, non-tumorigenic human mammary cell lines. Each genome-wide analysis contains profiles for six histone marks, methylated DNA, and RNA transcripts. Analysis of these datasets shows that each cell type has unique features, primarily within genomic regulatory regions, and that the cell lines group together. Analyses of the promoter and enhancer profiles place the luminal progenitors in between the basal cells and the non-progenitor luminal subset. Integrative analysis reveals networks of subset-specific transcription factors.