Abstract
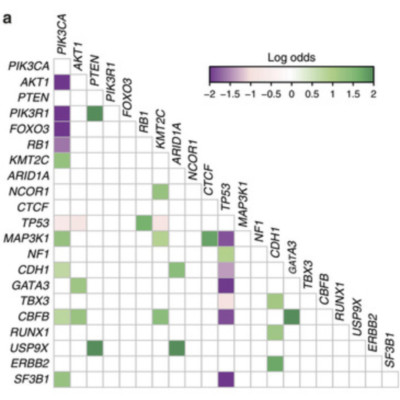
The genomic landscape of breast cancer is complex, and inter- and intra-tumour heterogeneity are important challenges in treating the disease. In this study, we sequence 173 genes in 2,433 primary breast tumours that have copy number aberration (CNA), gene expression and long-term clinical follow-up data. We identify 40 mutation-driver (Mut-driver) genes, and determine associations between mutations, driver CNA profiles, clinical-pathological parameters and survival. We assess the clonal states of Mut-driver mutations, and estimate levels of intra-tumour heterogeneity using mutant-allele fractions. Associations between PIK3CA mutations and reduced survival are identified in three subgroups of ER-positive cancer (defined by amplification of 17q23, 11q13-14 or 8q24). High levels of intra-tumour heterogeneity are in general associated with a worse outcome, but highly aggressive tumours with 11q13-14 amplification have low levels of intra-tumour heterogeneity. These results emphasize the importance of genome-based stratification of breast cancer, and have important implications for designing therapeutic strategies.