Abstract
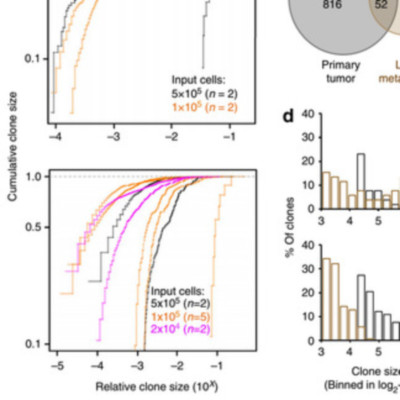
Genomic and phenotypic analyses indicate extensive intra- as well as intertumoral heterogeneity in primary human malignant cell populations despite their clonal origin. Cellular DNA barcoding offers a powerful and unbiased alternative to track the number and size of multiple subclones within a single human tumour xenograft and their response to continued in vivo passaging. Using this approach we find clone-initiating cell frequencies that vary from ~1/10 to ~1/10,000 cells transplanted for two human breast cancer cell lines and breast cancer xenografts derived from three different patients. For the cell lines, these frequencies are negatively affected in transplants of more than 20,000 cells. Serial transplants reveal five clonal growth patterns (unchanging, expanding, diminishing, fluctuating or of delayed onset), whose predominance is highly variable both between and within original samples. This study thus demonstrates the high growth potential and diverse growth properties of xenografted human breast cancer cells.