Abstract
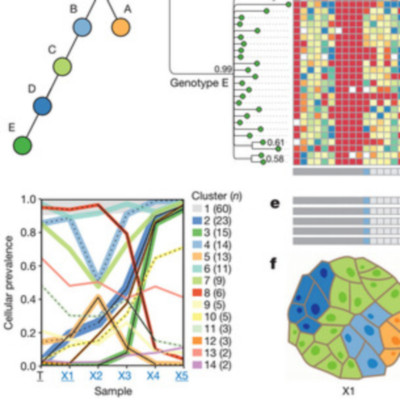
Human cancers, including breast cancers, comprise clones differing in mutation content. Clones evolve dynamically in space and time following principles of Darwinian evolution, underpinning important emergent features such as drug resistance and metastasis. Human breast cancer xenoengraftment is used as a means of capturing and studying tumour biology, and breast tumour xenografts are generally assumed to be reasonable models of the originating tumours. However, the consequences and reproducibility of engraftment and propagation on the genomic clonal architecture of tumours have not been systematically examined at single-cell resolution. Here we show, using deep-genome and single-cell sequencing methods, the clonal dynamics of initial engraftment and subsequent serial propagation of primary and metastatic human breast cancers in immunodeficient mice. In all 15 cases examined, clonal selection on engraftment was observed in both primary and metastatic breast tumours, varying in degree from extreme selective engraftment of minor (<5% of starting population) clones to moderate, polyclonal engraftment. Furthermore, ongoing clonal dynamics during serial passaging is a feature of tumours experiencing modest initial selection. Through single-cell sequencing, we show that major mutation clusters estimated from tumour population sequencing relate predictably to the most abundant clonal genotypes, even in clonally complex and rapidly evolving cases. Finally, we show that similar clonal expansion patterns can emerge in independent grafts of the same starting tumour population, indicating that genomic aberrations can be reproducible determinants of evolutionary trajectories. Our results show that measurement of genomically defined clonal population dynamics will be highly informative for functional studies using patient-derived breast cancer xenoengraftment.