Abstract
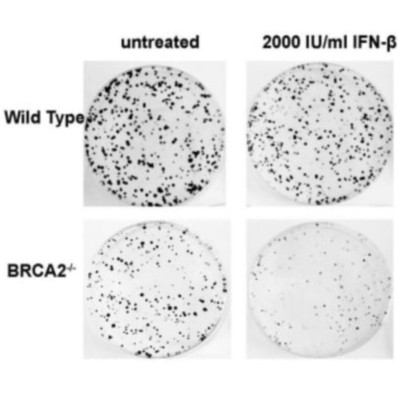
BRCA2 mutations are significantly associated with early-onset breast cancer, and the tumour-suppressing function of BRCA2 has been attributed to its involvement in homologous recombination (HR)-mediated DNA repair. In order to identify additional functions of BRCA2, we generated BRCA2-knockout HCT116 human colorectal carcinoma cells. Using genome-wide microarray analyses, we have discovered a link between the loss of BRCA2 and the up-regulation of a subset of interferon (IFN)-related genes, including APOBEC3F and APOBEC3G. The over-expression of IFN-related genes was confirmed in different human BRCA2(-/-) and mouse Brca2(-/-) tumour cell lines, and was independent of senescence and apoptosis. In isogenic wild-type BRCA2 cells, we observed over-expression of IFN-related genes after treatment with DNA-damaging agents, and following ionizing radiation. Cells with endogenous DNA damage because of defective BRCA1 or RAD51 also exhibited over-expression of IFN-related genes. Transcriptional activity of the IFN-stimulated response element (ISRE) was increased in BRCA2 knockout cells, and the expression of BRCA2 greatly decreased IFNα-stimulated ISRE reporter activity, suggesting that BRCA2 directly represses the expression of IFN-related genes through the ISRE. Finally, the colony-forming capacity of BRCA2 knockout cells was significantly reduced in the presence of either IFNβ or IFNγ, suggesting that IFNs may have potential as therapeutic agents in cancer cells with BRCA2 mutations. The GEO Accession No. for microarray analysis is GSE54830.