Abstract
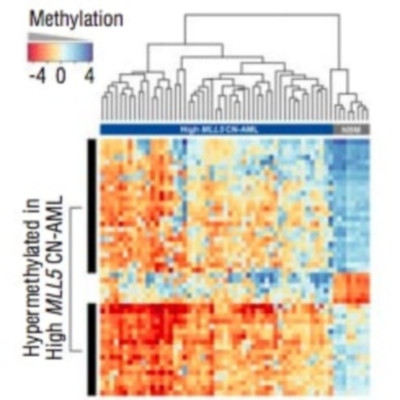
Hypomethylating agents are widely used in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes and unfit patients with acute myeloid leukemia. However, it is not well understood why only some patients respond to hypomethylating agents. We found previously that the effect of decitabine on hematopoietic stem cell viability differed between Mll5 wild-type and null cells. We, therefore, investigated the role of MLL5 expression levels on outcome of acute myeloid leukemia patients who were treated with decitabine. MLL5 above the median expression level predicted longer overall survival independent of DNMT3A mutation status in bivariate analysis (median overall survival for high vs. low MLL5 expression 292 vs. 167 days; P=0.026). In patients who received three or more courses decitabine, high MLL5 expression and wild-type DNMT3A independently predicted improved overall survival (median overall survival for high vs. low MLL5 expression 468 vs. 243 days; P=0.012). In transformed murine cells, loss of Mll5 was associated with resistance to low-dose decitabine, less global DNA methylation in promoter regions, and reduced DNA demethylation upon decitabine treatment. Together, these data support our clinical observation of improved outcome in decitabine-treated patients who express MLL5 at high levels, and suggest a mechanistic role of MLL5 in the regulation of DNA methylation.