Abstract
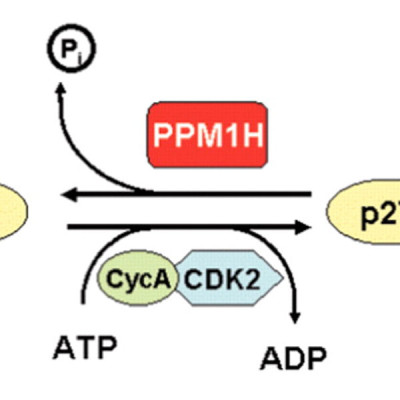
The HER2 oncogene is overexpressed or amplified in 20% of breast cancers. HER2-positive cancer historically portends a poor prognosis, but the HER2-targeted therapy trastuzumab mitigates this otherwise ominous distinction. Nevertheless, some patients suffer disease recurrence despite trastuzumab, and metastatic disease remains largely incurable due to innate and acquired resistance. Thus, understanding trastuzumab resistance remains an unmet medical need. Through RNA interference screening, we discovered that knockdown of the serine/threonine phosphatase PPM1H confers trastuzumab resistance via reduction in protein levels of the tumor suppressor p27. PPM1H dephosphorylates p27 at threonine 187, thus removing a signal for proteasomal degradation. We further determined that patients whose tumors express low levels of PPM1H trend towards worse clinical outcome on trastuzumab. Identifying PPM1H as a novel p27 phosphatase reveals new insight into how cancer cells destabilize a well-recognized tumor suppressor. Furthermore, low PPM1H expression may identify a subset of HER2-positive tumors that are harder to treat.