Abstract
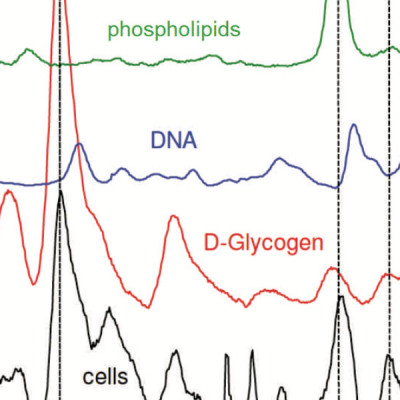
Measuring spatial and temporal patterns of cytochemical variation in human embryonic stem cell (hESC) colonies is necessary for understanding the role of cellular communication in spontaneous differentiation, the mechanisms of biological niche creation, and structure-generating developmental processes. Such insights will ultimately facilitate directed differentiation and therewith promote advances in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. However, the patterns of cytochemical inhomogeneities of hESC colonies are not well studied and their causes are not fully understood. We used Raman spectroscopic mapping to contrast supracellular variations in cytochemical composition across pluripotent and partly differentiated hESC colonies to gain a better understanding of the early-stage (i.e., 5 days) effects of the differentiation process on the nature and evolution of these patterns. Higher protein-to-nucleic acid ratios, a differentiation status indicator observed previously using Raman spectroscopy, confirmed reported results that spontaneous differentiation is more pronounced on the edges of a colony than elsewhere. In addition, pluripotent and partly differentiated colonies also showed higher lipid concentrations relative to nucleic acids at colony edges in contrast to relative glycogen concentrations, which were up to 400% more pronounced in the colony centers compared to their edges. Pluripotent and partly differentiated colonies differed, with the latter having higher average protein-to-nucleic acid and lipid-to-nucleic acid ratios but a lower glycogen-to-nucleic acid ratio. In both cases, cell density, pluripotency, and high glycogen appeared to vary in tandem. Spatial variations in glycogen- and protein-to-nucleic acid ratios have features on the order of 100 μm and larger. These dimensions are consistent with those reported for stem cell niches and suggest that cytochemical inhomogeneities may provide colony-level information about niches and niche formation. These results demonstrate Raman mapping to be a potentially useful technique for revealing the complexities in the spatial organization of hESC cultures and thus for monitoring the evolution of engineered hESC niches.