Abstract
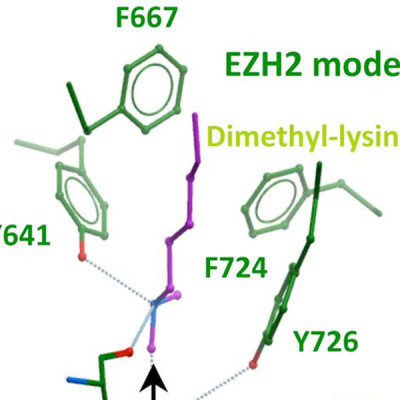
Next-generation sequencing of follicular lymphoma and diffuse-large B-cell lymphoma has revealed frequent somatic, heterozygous Y641 mutations in the histone methyltransferase EZH2. Heterozygosity and the presence of equal quantities of both mutant and wild-type mRNA and expressed protein suggest a dominant mode of action. Surprisingly, B-cell lymphoma cell lines and lymphoma samples harboring heterozygous EZH2(Y641) mutations have increased levels of histone H3 Lys-27-specific trimethylation (H3K27me3). Expression of EZH2(Y641F/N) mutants in cells with EZH2(WT) resulted in an increase of H3K27me3 levels in vivo. Structural modeling of EZH2(Y641) mutants suggests a “Tyr/Phe switch” model whereby structurally neutral, nontyrosine residues at position 641 would decrease affinity for unmethylated and monomethylated H3K27 substrates and potentially favor trimethylation. We demonstrate, using in vitro enzyme assays of reconstituted PRC2 complexes, that Y641 mutations result in a decrease in monomethylation and an increase in trimethylation activity of the enzyme relative to the wild-type enzyme. This represents the first example of a disease-associated gain-of-function mutation in a histone methyltransferase, whereby somatic EZH2 Y641 mutations in lymphoma act dominantly to increase, rather than decrease, histone methylation. The dominant mode of action suggests that allele-specific EZH2 inhibitors should be a future therapeutic strategy for this disease.